My astrophysical research interests are broadly focused on white dwarf stars, the final stage for essentially every star we know that hosts planets within the Milky Way, including our own Sun in T-minus 5 billion years. Through studying how some of these ancient, retired stars are changing brightness, I seek to learn about the surviving planetary systems they harbor. I am looking for the carcasses of extrasolar asteroids and rocky planets manifest as clouds of debris orbiting very close to the star. I study how these planetary debris orbit around these stars to learn about the dynamics of remnant planetary systems. Each of these systems is gradually accreting this planetary debris. The spectra of these stars can be exploited to take an inventory of the chemical species comprising the debris, allowing us to test the geochemical similarity between these extrasolar rocks and those of our own Solar System.
Here I highlight the published research projects I have contributed to, including peer-reviewed journal articles and research posters.
My ORCiD is available at:
An ADS library of my literature is accessible at this link.
First-authored Refereed Publications:
Joseph Guidry, JJ Hermes, Kishalay De, et al. 2024, ApJ, 972, 126. – Using 3.4-micron Variability toward White Dwarfs as a Signpost of Remnant Planetary Systems
White dwarfs that are accreting from debris disks are siphoning sublimated debris onto their photospheres. While over 40% of white dwarfs show metal lines in their spectra indicative of accretion, fewer than 0.1% of white dwarfs shows evidence for a circumstellar gas disk. Separately, 2% of white dwarfs show infrared excesses consistent with dusty debris disks (all of which are metal polluted, and all gas disks show dusty components). It has been known that the systems that do show gaseous emission show the most variable emission at 3.4 microns, indicating the dusty component of the debris disk is highly dynamic. This lends credence to the theory that these systems show gasd becuase collisional cascades are liberating enough material to be sublimated to be viewed. We seek to test the hypothesis that white dwarfs showing gaseous emission characteristically are the most collisionally active and therefore more variable at 3.4 microns than any other category of white dwarfs. We use a novel pipeline to extract light curves from the unWISE images from the NEOWISE mission (2013-2023) to rank the variability of light curves from samples of white dwarfs showing gaseous emission, those showing infrared excesses from dusty disks, over 3000 bright Gaia white dwarfs within 100 pc, and a control sample of highly variable cataclysmic variables. After quality filtering, the gas disk systems are indeed the most variable, only eclipsed by the cataclysmic variables, and the dusty white dwarfs are more variable than the general field stars, agreeing with the results of previous work. We begin a preliminary campaign to follow-up our most variable Gaia white dwarfs in effort to detect new gas disks. Only 1/7 out of sources shows metal pollution at the calcium II triplet, indicating the system is harboring a debris disk. None of the seven show gaseous emission. Our catalog of variables features over 80 new near-infrared variable white dwarfs and is available at this Zenodo, along with all of the light curves we generated for our study.
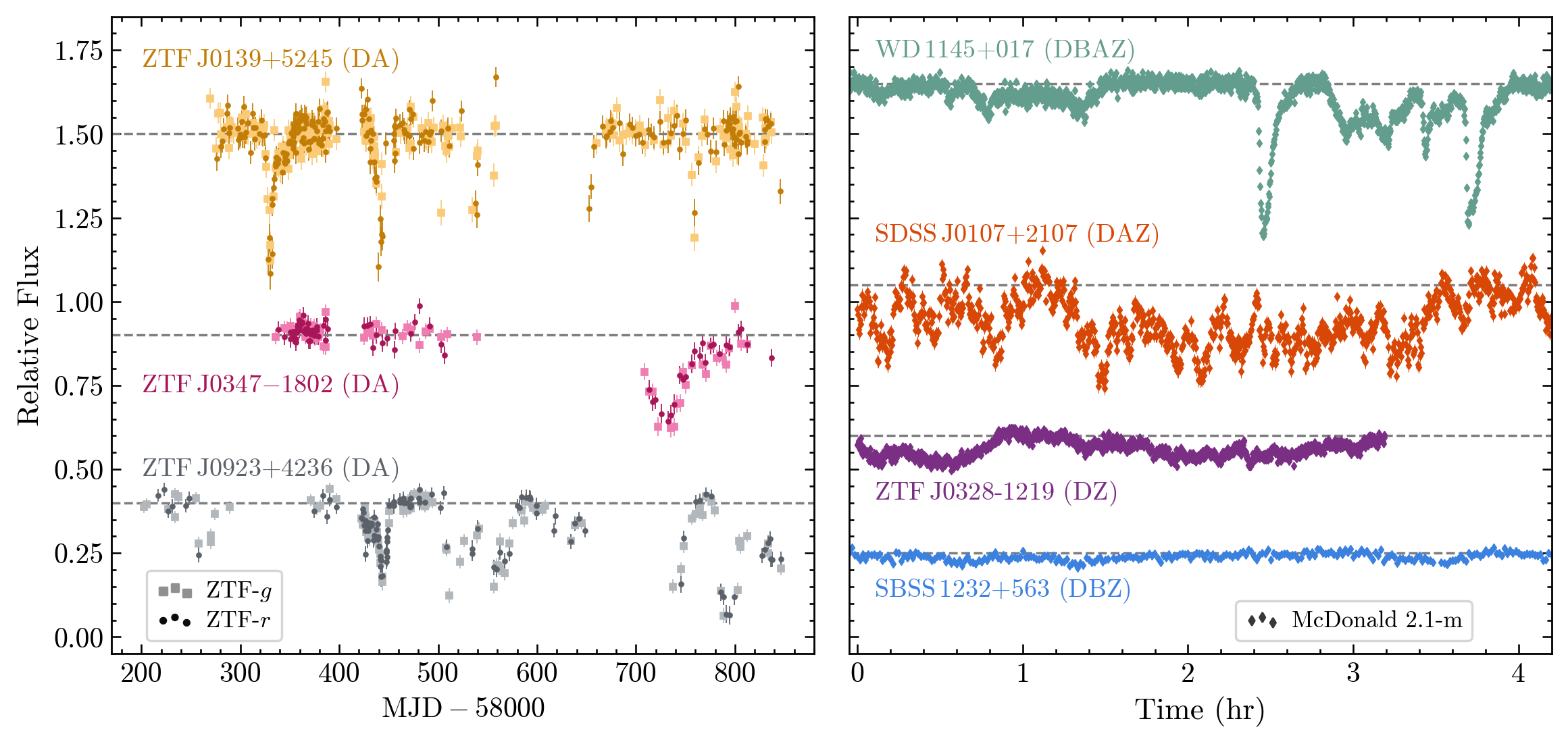
Joseph Guidry, Zachary Vanderbosch, JJ Hermes, et al. 2021, ApJ, 912, 125. – I Spy Transits and Pulsations: Empirical Variability in White Dwarfs Using Gaia and the Zwicky Transient Facility
In our paper we use anomalous levels of excess scatter in Gaia DR2 and the Zwicky Transient Facility photometry as a proxy for variability. We use our variability metrics to rank ~12,100 white dwarf stars centered on a parameter space known as the ZZ Ceti instability strip, where hydrogen-atmosphere (DA) white dwarfs are observed to pulsate. As a proof of concept, we investigated the top 1% (121 white dwarfs) ranked by our metrics, recovering 39 white dwarfs previously known to “go bump in the night.” Our follow-up high-speed photometry from the McDonald Observatory 2.1m Telescope confirmed variability in 33 out of 33 observed candidates from the top 1%, further establishing our efficacy and sensitivty. Most excitingly, in the top 1% we recovered the two white dwarfs previously known to host transiting planetary debris (WD 1145+017 - top right, and ZTF J0139+5245, top left) and find evidence in our follow-up photometry (right) and ZTF light curves (left) for 5 more systems demonstrating transits on varying timescales. We obtained indetifying spectra for three of systems, ruling out variability indicative of a cataclysmic variable, while SDSS J0107+2107 and SBSS 1232+536 exhibited metal pollution in prior SDSS spectra. These objects should be closesly monitored to confirm their candicacy and probe for substrcutres and repeating patterns in observations of future transits. Lastly, we cofirm 29 new ZZ Ceti pulsators, find possible the closest known polar at ~56 pc away (ZTF J0146+4914), and one possible spotted-magnetic variable white dwarf (ZTF J0534+7707). Hope you enjoy the results!
Refereed Publications as Contributing Author:
Steen, M., Hermes, J. J., Guidry, J. A., et al. 2024, ApJ 967, 166 – Measuring White Dwarf Variability from Sparsely Sampled Gaia DR3 Multi-epoch Photometry
Farihi, J., Hermes, J. J., Marsh, T. R., …, Guidry, J. A. (author 6/14), et al. 2022, MNRAS, 511, 1647. – Relentless and complex transits from a planetesimal debris disc.
Vanderbosch, Z. P., Rappaport, S., Guidry, J. A., et al. 2021, ApJ, 917, 41. – Recurring Planetary Debris Transits and Circumstellar Gas around White Dwarf ZTF J0328-1219
Kupfer, T., Prince, T. A., van Roestel, J., …, Guidry, J. A. (author 18/21), et al. 2021, MNRAS, 505, 1254. – Year 1 of the ZTF high-cadence Galactic plane survey: strategy, goals, and early results on new single-mode hot subdwarf B-star pulsators
Research Posters:
Joseph Guidry, Zachary Vanderbosch, JJ Hermes, Mike Montgomery - Searching for Color Changes During Outburst
This worked has been presented at multiple conferences, inlcuding the TASC5/KASC12 (the TESS and Kepler Asteroseismic Consortiums), and Bash Fest 2019 and the Undergrad Research Forum at UT Austin. Using Pan-STARRS multicolor photometry and K2 photometry, we attempted to assess the changes of color as a result of outburst for two outbursting ZZ Ceti whit dwarfs. Aside from confirming the expectation that white dwarfs are indeed bluer during at the peaks of pulsations than in troughs or in quiescence, definitive results have been found yet. It appears new Pan-STARRS pipelines offered by the Mikulski Archive have developed a work around that plagued our analysis.
You can view our poster here.
 https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9632-7347
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-9632-7347